Oracle Grid Infrastructure 19c (Oracle Restart) Installation
- Ömercan Çalım
- Aug 25, 2025
- 8 min read
Updated: Aug 28, 2025

Requirements
Oracle Linux 8.10
Oracle Grid Infrastructure 19c (GI) zip file
Oracle Database 19c (DB) zip file
VirtualBox 7.1
Vitrual Machine resource allocation:
5 GB RAM
1 Cores [CPU]
70 GB Virtual Disk for OS
30x2 GB Virtual Disk for ASM
Steps
Set up the Virtual Machine
Cloning existing VM and Adding Virtual Disk
OS preparation for GI and DB Installation
Configuring disks to be used by Automatic Storage Management as disk groups
Oracle Grid Infrastructure 19c (Standalone Server) installation
Creating FRA disk group using ASMCA
Oracle Database 19c Software Only installation
Creating Database using DBCA
Set up the Virtual Machine
I strongly recommend creating a new virtual machine by cloning an existing one. This way, if you ever want to start from the beginning, you won’t need to reinstall the operating system. Make sure that base machine at least 60 GB disk space. For more details see Oracle Linux 8.10 Installation using VirtualBox 7.1.
Cloning existing VM and Adding Virtual Disk
Select a virtual machine and right-click.
Choose the clone option.
Name your machine.
Choose the path where you want to store your virtual machine.
Select full clone.
Choose the generate new MAC addresses option. This is the best option when both the source VM and the cloned VM must operate on the same network.
Click finish.


When cloning is finished, open settings of your cloned VM and add virtual disks.
Open settings for the cloned VM.
Navigate to the storage tab.
Click the add hard disk button.
Select create.
Specify 30 GB for the disk size.
Make sure pre-allocate full size option is unchecked.
Click finish.
Under the not attached tab, select the newly created disk.
Repeat these steps to add another 30 GB virtual disk.
Start VM.





Prepare the OS for GI and DB Installation
Throughout this article, some Oracle standard configuration settings will be modified or not strictly followed such as using a single OS user (oracle) as the administrator for both Grid Infrastructure components and the Oracle Database. These adjustments are neither mandatory nor critical but they aim to improve ease of use and enhance understanding. Once you are familiar with the workflow and the relationships between components, you can modify these settings by performing a fresh installation.
Login as root user.
make sure you have internet connection
# ping www.google.comInstall Oracle prerequisites packages, if you wonder where those packages are installed, you can run the "dnf repolist" command also run the "dnf list" command to display installed packages.
display packages
# dnf list
display repositories
# dnf repolist
install oracle prereqisites
# dnf install oracle-database-preinstall-19c -y

optional, upgrade your system
# dnf check-update
# dnf upgrade Ensure that "oracle" user is a member of necessary OS groups.
"id" command prints real and effective user and group IDs
# id oracle
create OS groups for ASM administration and operation
# groupadd -g 54327 asmdba
# groupadd -g 54328 asmoper
# groupadd -g 54329 asmadmin
add oracle user to the created secondary groups
# usermod -a -G asmadmin,asmdba,asmoper oracle
change the password of oracle user
# passwd oracle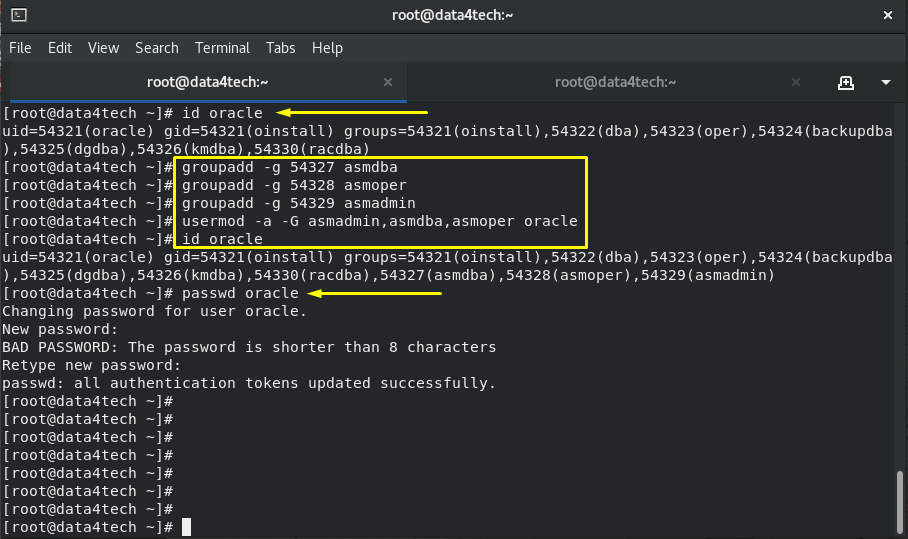
Below are the OS groups used to manage and operate Oracle Grid Infrastructure (GI) and Oracle Database (DB)
oinstall is primary group, others are secondary group
also known as Oracle Inventory group. grants all system privileges for Oracle Clusterware, Oracle ASM and Oracle Databases on the servers. Also all system privileges for installation owners.
54421 oinstall
grants privileges to administer the database
54322 dba
grants limited set of database administrative privileges
54323 oper
grants privileges to perform backup and recovery operations using RMAN or SQL*Plus
54324 backupdba
grants privileges to perform Data Guard operations
54325 dgdba
grants privileges to perform Transparent Data Encryption keystore operations.
54326 kmdba
allows access the Oracle ASM disk devices
54327 asmdba
grants startup and shutdown privileges of Oracle ASM.
54328 asmoper
grants privileges to administer Oracle ASM.
54329 asmadmin
grants privileges to perform administration of Oracle databases on an Oracle RAC cluster.
54330 racdba Create the directories for the Oracle GI and Oracle DB installation
oracle base
# mkdir -p /u01/app/oracle
oracle home
# mkdir -p /u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1
grid base
# mkdir -p /u01/app/grid
grid home
# mkdir -p /u01/app/19.0.0/grid
change the directory owner, group and mode
# chown -R oracle:oinstall /u01
# chmod -R 775 /u01
permissions of 775 are required for installation and may be changed during the installation process. Ownership and these permissions allow Oracle Universal Installer (OUI) to create the Oracle Inventory directory at /u01/app/oraInventory.
# ll /u01
# ll /u01/app
Switch to the oracle user, take a backup of .bash_profile file.
# su - oracle
cd ~ same as cd /home/oracle
$ cd /home/oracle
$ cp .bash_profile .bash_profile.bkpCreate .grid_env file in /home/oracle with the required Oracle GI environment variables, alternatively using cat.
$ cat > /home/oracle/.grid_env <<EOF
paste the following text
# Environment variables
ORACLE_SID=+ASM; export ORACLE_SID
ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/grid; export ORACLE_BASE
ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/19.0.0/grid; export ORACLE_HOME
ORACLE_TERM=xterm; export ORACLE_TERM
JAVA_HOME=/usr/bin/java; export JAVA_HOME
TNS_ADMIN=\$ORACLE_HOME/network/admin; export TNS_ADMIN
PATH=.:\${JAVA_HOME}/bin:\${PATH}:\$HOME/bin:\$ORACLE_HOME/bin
PATH=\${PATH}:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/bin
export PATH
# setting the mask to 022 ensures that the user performing the software installation creates files with 644 permissions
umask 022
EOF
Create .db19c_env file in /home/oracle with the required Oracle DB 19c environment variables
$ cat > /home/oracle/.db19c_env <<EOF
# Environment variables
ORACLE_HOSTNAME=\$HOSTNAME; export ORACLE_HOSTNAME
ORACLE_SID=d4tdb; export ORACLE_SID
ORACLE_UNQNAME=d4tdb; export ORACLE_UNQNAME
ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle; export ORACLE_BASE
ORACLE_HOME=\$ORACLE_BASE/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1; export ORACLE_HOME
ORACLE_TERM=xterm; export ORACLE_TERM
JAVA_HOME=/usr/bin/java; export JAVA_HOME
TNS_ADMIN=\$ORACLE_HOME/network/admin; export TNS_ADMIN
PATH=.:\${JAVA_HOME}/bin:\${PATH}:\$HOME/bin:\$ORACLE_HOME/bin
PATH=\${PATH}:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/bin
NLS_DATE_FORMAT="DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS"; export NLS_DATE_FORMAT
TEMP=/tmp ;export TMP
TMPDIR=\$tmp ; export TMPDIR
export PATH
umask 022
EOFAppend the commands to the .bash_profile file and apply.
$ echo "source ~/.grid_env" >> ~/.bash_profile
$ echo "source ~/.db19c_env" >> ~/.bash_profile
$ source /home/oracle/.bash_profile
$ . .db19c_env
$ echo $ORACLE_HOME
Check the NTP service
switch to root user
$ su - root
check the NTP service (to ensure your system clock stays accurate)
# systemctl status chronyd
# systemctl start chronyd
check the current synchronization status
# chronyc tracking
Set SELinux to permissive to prevent it from potentially blocking required operations such as file access, network calls, and shared memory.
change SELINUX=enforcing to SELINUX=permissive
# sed -i s/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=permissive/g /etc/selinux/config
# sed -i s/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g /etc/selinux/config
# cat /etc/selinux/config | grep SELINUX
# setenforce Permissive
stop the firewall and disable it
# systemctl stop firewalld
# systemctl disable firewalld
Set up disks to be used by Automatic Storage Management as disk groups
Oracle ASM expects each disk group device to be on a separate physical disk.
# lsblk
Now, we will set up OS disks to be used as disk groups by Oracle ASM. By running the lsblk command, block devices can be listed. You can see the initial 70 GB and 30 GB disks as sda, sdb, and sdc
# udevadm info -a /dev/sdb | grep -i kernel=
# udevadm info /dev/sdb | grep -i devtype
# /lib/udev/scsi_id -gud /dev/sdb
# udevadm info -a /dev/sdc | grep -i kernel=
# udevadm info /dev/sdc | grep -i devtype
# /lib/udev/scsi_id -gud /dev/sdc
open a new terminal
you can maintain storage file path persistence by creating a rules file
create and edit the rules file for devices
# vim /etc/udev/rules.d/99-asm-disks.rules
since Oracle Restart (but not Oracle Clusterware) will be installed, OCR and Oracle GIMR disk groups do not need to be configured. The DATA and FRA disk groups are sufficient for now.
paste below text to the file
DO NOT FORGET TO CHANGE the "RESULT" parameter which should be set to the output of "/lib/udev/scsi_id -gud" command
KERNEL=="sd*", OWNER="oracle", GROUP="asmadmin", MODE="0660", ENV{DEVTYPE}=="disk", PROGRAM=="/lib/udev/scsi_id -gud /dev/$name", RESULT=="1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VB6c2e1f8d-2d9c2549", SYMLINK+="oracleasm/DAT_ASM_1"
KERNEL=="sd*", OWNER="oracle", GROUP="asmadmin", MODE="0660", ENV{DEVTYPE}=="disk", PROGRAM=="/lib/udev/scsi_id -gud /dev/$name", RESULT=="1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VB801f4283-df18b664", SYMLINK+="oracleasm/FRA_ASM_1"

# fsck -N /dev/sdb
# fsck -N /dev/sdc
reload the UDEV rules
# udevadm control --reload-rules && udevadm trigger --action=add
# ll /dev | grep -e sdb -e sdc
# ll /dev/oracleasm/
Installing Oracle Grid Infrastructure 19c (Standalone Server)
Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a standalone server also known as Oracle Restart
supports single instance databases, includes Oracle Restart and Oracle Automatic Storage Management (ASM). This support includes volume management, file system, and automatic restart capabilities. Install Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a standalone server, which installs Oracle Restart and Oracle ASM, and creates one disk group.
Oracle Restart is currently restricted to manage single instance Oracle Databases and Oracle ASM instances only. Oracle Restart improves the availability of your Oracle database by providing the following services:
When there is a hardware or a software failure, Oracle Restart automatically starts all Oracle components, including the Oracle database instance, Oracle Net Listener, database services, and Oracle ASM.
Oracle Restart starts components in the proper order when the database host is restarted.
Oracle Restart runs periodic checks to monitor the status of Oracle components. If a check operation fails for a component, then the component is shut down and restarted.
Download related files from Oracle downloads for Linux page.


Transfer the installed zip files using one of the following tools scp , ftp or sftp then unzip the files
open "cmd" on your Windows machine
> which scp
change IP address as your VM IP addreess
> scp D:\Storage\LINUX.X64_193000_grid_home.zip oracle@192.168.0.25:/u01/app/19.0.0/grid
> scp D:\Storage\LINUX.X64_193000_db_home.zip oracle@192.168.0.25:/u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1If you got "WARNING: REMOTE HOST IDENTIFICATION HAS CHANGED!" error, run below command and try again. Running it clears old key entry so you can connect again without the mismatch error.
ssh-keygen -R 192.168.0.25
> ssh-keygen -R <host> 

Switch to oracle user

set grid environment variables
$ . .grid_env
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME
$ ll
$ unzip LINUX.X64_193000_grid_home.zip
Configure X11 forwarding by setting the display environment
open a new terminal and switch to root user
$ su - root
# xdpyinfo | head
run below commands as oracle user
$ export DISPLAY=:1.0
$ xhost +
to test the x11 forwarding run below command
$ xev
$ export CV_ASSUME_DISTID=OEL7.6
run GI installer
$ ./gridSetup.sh




Redundancy option determines how many copies of your data files, control files, online log files and archived log files are kept. The External means no copies are kept, only the original ones are stored.

Set the discovery path as the path defined in the 99-asm-disks.rules file.













open a new terminal and switch to root user then run the required scripts
$ su - root
# sh /u01/app/oraInventory/orainstRoot.sh
# sh /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/root.sh



When installation is successfully completed run the following command:
crsctl stat res -tCRSCTL is an Oracle Restart/Clusterware specific utility. It manages the Oracle High Availability Services stack in the Oracle Restart environment, which consists of the Oracle High Availability Services daemon (ohasd), Oracle ASM (if installed), and Cluster Synchronization Services (if Oracle ASM is installed). In Oracle Restart environment CRSCTL commands only affect the local server on which you run them.
Focus on local resources for now:
ora.DATA.dg created disk group named as DATA
ora.LISTENER.lsnr Oracle Net Listener
ora.asm asm instance
Creating FRA Disk Group using ASMCA
run below command in the same terminal
$ asmca



$ crsctl stat res -t
Installing Oracle Database 19c Software Only
Unzip the Oracle Database 19c zip file in the Oracle home directory.
cd ~
$ cd /home/oracle
set database environment variables
$ . .db19c_env
$ echo $ORACLE_HOME
$ /u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME
$ ll
$ unzip LINUX.X64_193000_db_home.zip
get the display value as described earlier
$ export DISPLAY=:1.0
$ export CV_ASSUME_DISTID=OEL7.6
run Oracle DB installer
$ ./runInstaller








open a new terminal and switch to root user
$ su - root
# sh /u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1/root.sh

Creating Database Using DBCA
run database configuration assistant (dbca)
$ dbca
if you get following error navigate to the bin directory and run dbca again ($ORACLE_HOME/bin)
$ cd bin






About Fast Recovery Area and Fast Recovery Area Disk Group
Oracle Database writes all RMAN backups, archive logs, control file automatic backups, and database copies to the fast recovery area. Fast recovery area size is set to 29 GB because the disk used to create FRA disk group was 30 GB.




Number of processes may vary for your installation

You may leave this step with default parameters or choose the language you want to set up for your database









$ cd ~
$ . .grid_env
$ crsctl stat res -t
$ . .db19c_env
try to connect database
$ sqlplus / as sysdba
SQL> select 1 from dual;
SQL> select open_mode from v$database;
SQL> exit
$ . .grid_env
run ASM Command-Line Utility
$ asmcmd
check the file directories
See the following Oracle documents for advanced information

Comments